Advanced Materials and Electrochemistry for Energy Laboratory
Advanced Materials and Electrochemistry for Energy (AMEE) Laboratory investigates performance of materials for electrochemical energy storage and conversion systems.
Li-ion Batteries:
Lithium (Li)-ion batteries dominates the current landscape of energy storage for portable electronics. However, more demanding applications such as electrical vehicles requires fast charging of Li-ion batteries, which causes performance loss.
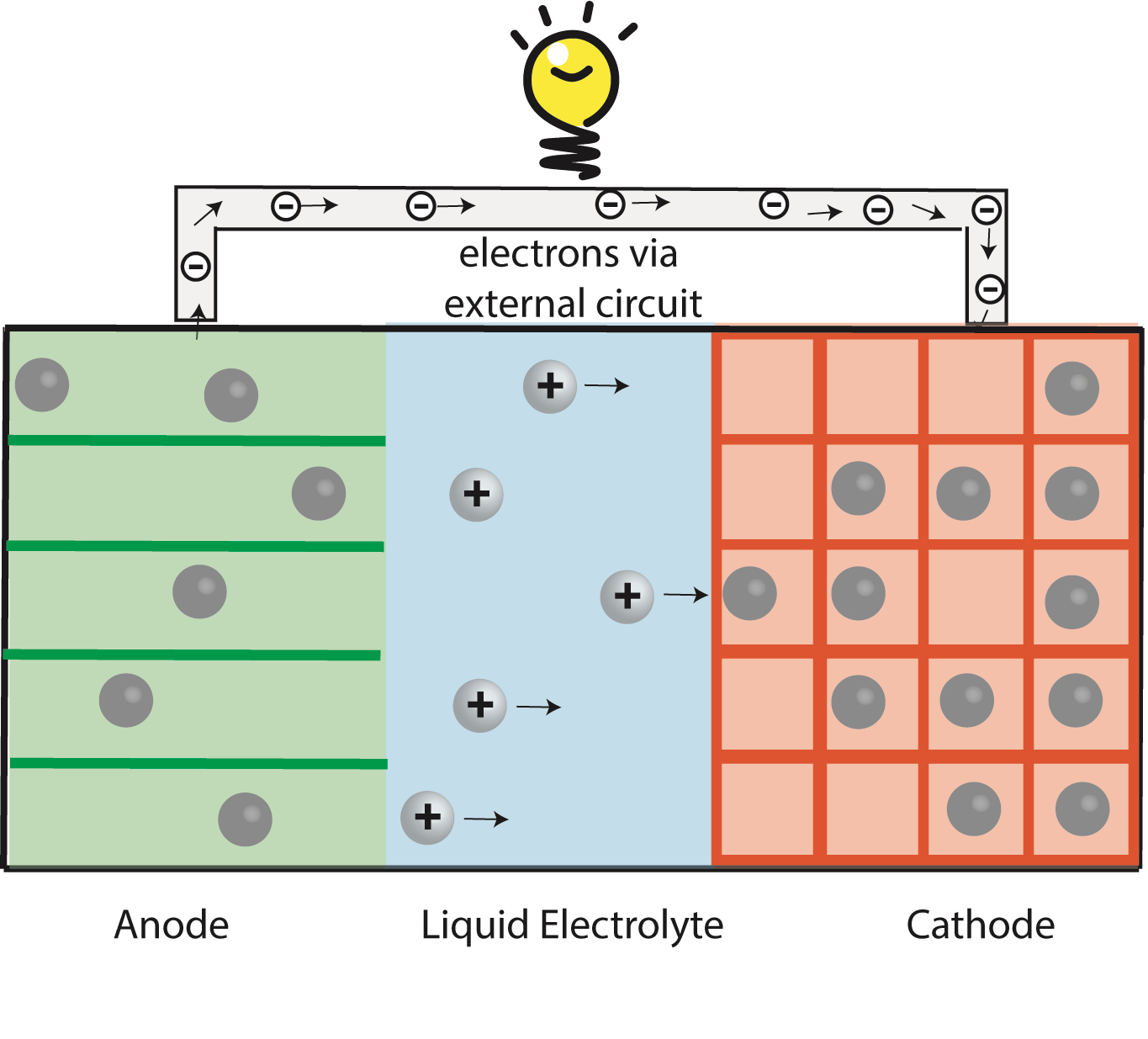
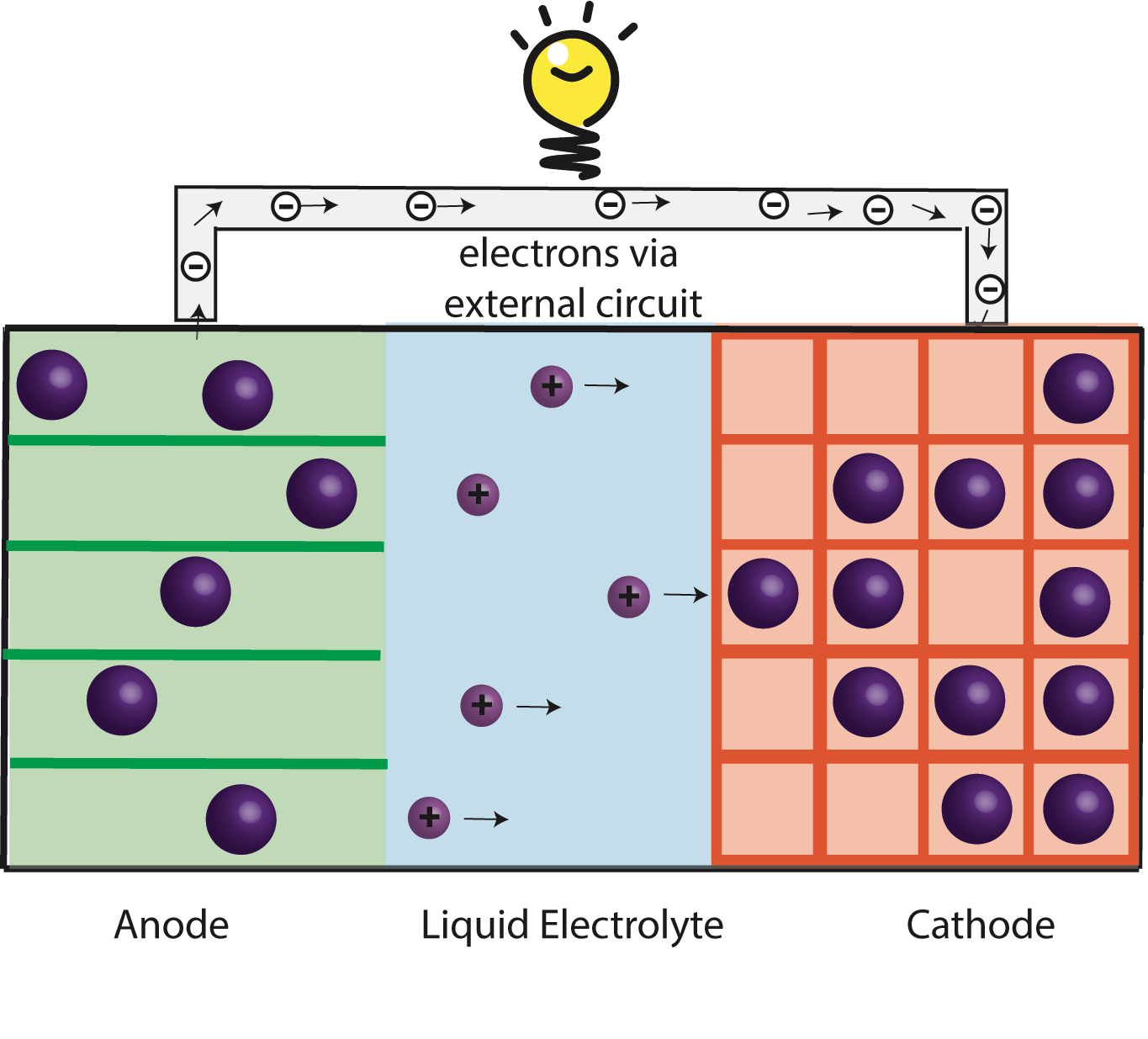
Na-ion & K-ion Batteries:
Replacing Li with more abundant Sodium (Na) or Potassium (K) can reduce cost of batteries for stationary applications. Na-ion and K-ion batteries requires new material chemistries because they are larger and heavier compared to Li ions.
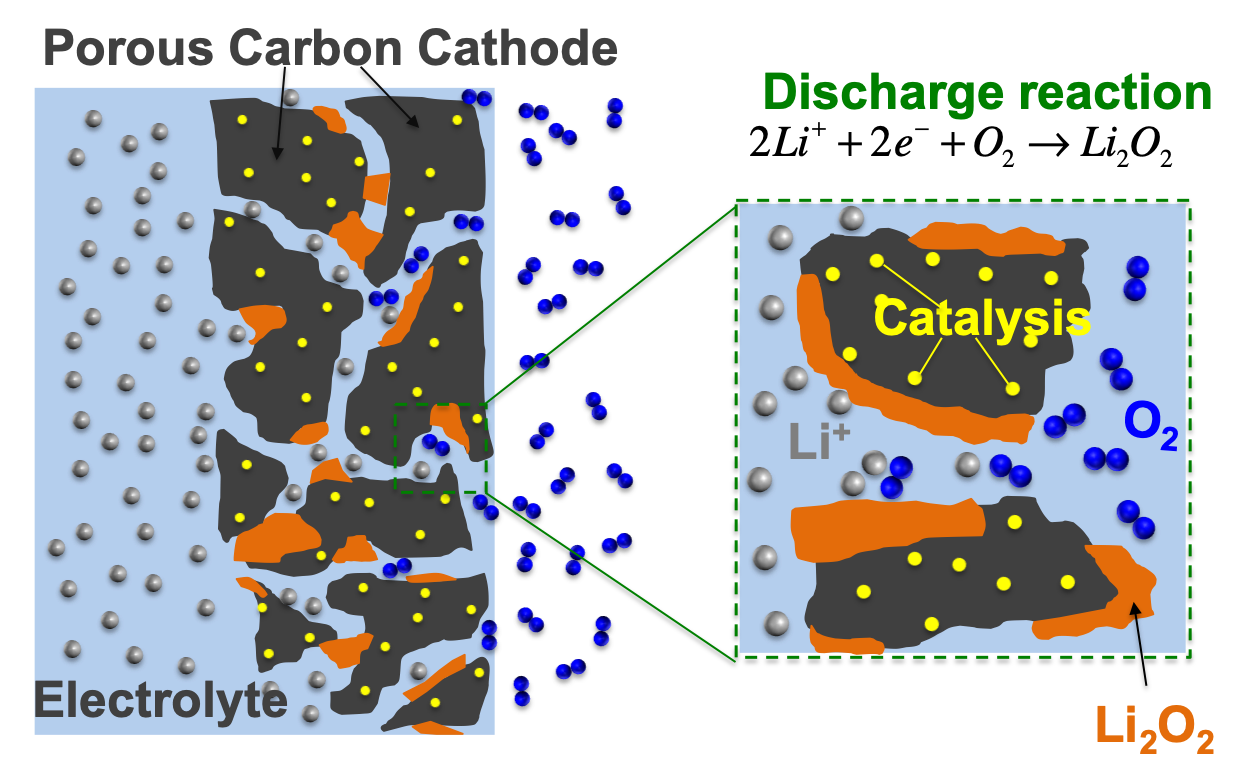
Li-Oxygen Batteries:
Lithium Oxygen batteries have higher theoretical capacity compared to Li-ion batteries. However, irreversible parasitic reactions and poor understanding of surface chemistries prevents reaching its theoretical capacities.
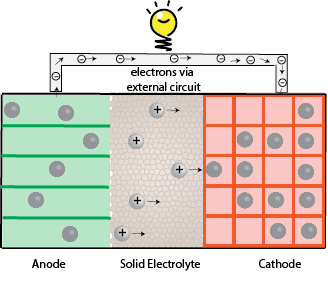
Solid Electrolytes:
Replacing organic liquid electrolytes in Li-ion batteries with solid electrolytes can prevent batteries catching fire and allow new battery chemistries. However, interfacial instabilities between electrolyte – electrode is the bottleneck of solid electrolytes.
News
Follow Dr. Özgür Çapraz on X (twitter), Bluesky and Linkedn.
Department of Chemical, Biochemical & Environmental Engineering
UMBC, Engineering Building Room 314
Baltimore, MD 21250
410-455-3400






